MySQL Database
MySQL has become one of the most popular database management systems in the world. It can be used for small development projects to large and prestigious sites on the web. MySQL has proven itself to be solid, reliable, fast and trusted to all sorts of data storage needs.
MySQL and MariaDB are open source and free to use. This makes it one of the most popular databases. It is also the best supported and best documented database for web based projects. For example with PHP.

MySQL vs MariaDB
MySQL is maintained by Oracle. MySQL is free to use but not entirely open source. Some parts are closed source. This was not the vision of the original developers. Therefor they created a fork that replaces the closed source parts with open source alternatives. This fork is called MariaDB, and guarantees to stay open source.
MariaDB and MySQL are therefor compatible. All MySQL command are compatible with MariaDB and vica versa.
What is a database?
The word database is used in many ways. For our purpose we will use the following definition:
A database is a collection of data stored in some organized fashion
You can think of a database as some kind of cabinet. It is simply a physical location to store data, regardless of what data is or how it is stored.
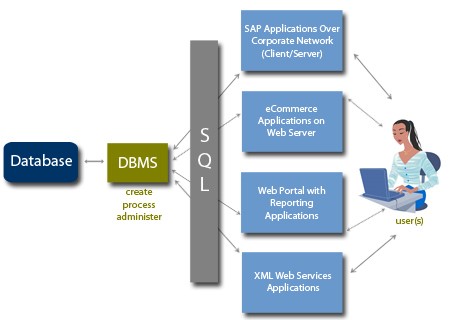
DataBase Management System - DBMS
The term database does not refer to the database software that is used. This might create much confusion if not used correctly. The database software is called the Database Management System or DBMS.
The database is the container that is created and can be manipulated using the DBMS. MySQL in this case is a DBMS system, not the fysical database.
A database might be a file on a hard drive, but it might not. It is not even significant as you never access a database directly anyway. You always use the DBMS that accesses the database for you.
Tables
When storing information in a filing cabinet, you don’t just toss it in a drawer. You create files within the cabinet. You file related data in specific files.
In the database world, the file is called a table. A table is a structured file that can store data of a specific type. A table may contain a list of customers, a product catalog or any other list of information.

Columns and datatypes
Tables are made up of columns. Columns contain a particular piece of information within the table. You can envision database tables as grids (like spreadsheets). Each column on the grid contains a particular piece of information.
Each column in a database has an associated datatype. It defines what the type the data the column can contain
Eg: Numeric, date, text, currency,…
Datatypes are very important for a database. They restrict the type of data that can be stored in the column, preventing wrong information to be stored. It can also help sorting the data correctly and efficiently. They play an important role in optimizing disk usage.
Rows
Data in a table is stored in rows. Each record saved is stored in its own row.
Eg: A customer table might store one customer per row
The number of rows in the table is the number of records in it. Record and row are used interchangeably but row is technically the correct term.
SQL
SQL pronounced as:
- Letters: S-Q-L
- Or as SEQUEL (Structured English Query Language) original name.
Stands for Structured Query Language and is a language that is designed specifically for communicating with databases. Unlike other languages (spoken languages, or programming languages such as Java or C++) SQL is made up of very few words. This is deliberate. SQL is designed to do one thing, and do it very well. SQL provides you with a simple and efficient way to read and write data from a database.
Advantages
SQL is not proprietary. It is not used by specific database vendors. Almost every major DBMS system supports SQL. This enables you to interact with just about every database you’ll run into.
SQL is easy to learn. The statements are all made up of descriptive English words (and there aren’t many of them). Despite its apparent simplicity, SQL is actually very powerful. Cleverly using its language elements, you can perform very complex and sophisticated database operations.
Installation
MySQL can be installed using the apt package manager with the following command:
sudo apt install mysql-server php-mysql -y
sudo service apache2 restart
2
MySQL client
You can now start the MySQL client using the terminal.
sudo mysql -u root
mysql: this tells your commandpromp or powerschell to start the mysql client.-u root: the -u tells the client to log with the given name, in this case 'root'.-p: the -p tells the client to ask for a password after you pressed enter.-h 127.0.0.1: this tells the client to connect on ip-adress127.0.0.1, can be used for connection on remote servers, when not specified it will use localhost.
You should be connected now and see
MariaDB [(none)]>
Trying out some queries
Using SQL we can do alot of things. The two most used types of queries are:
- Data definition: This defines how data is stored. What tables the database contains, how te tables are structured, what properties and data types do the columns have.
- Data manipulation: Creating, Reading, Updating and Deleting data (CRUD).
Data definition
Data definition language (DDL) statements are used for creating tables, relationships and other structures.
Before we can do anything in SQL we need to create a database. This can be done with the CREATE DATABASE query.
CREATE DATABASE bookstore;
Now we have a database that can group tables and there data. We just need to create a new table with the CREATE TABLE query. The query needs a table name, books in this example. Next we need to define the different columns that will exist in the table. Each column has a name, datatype and some extra properties.
To create a table that can store data about books, like ISBN, name, description and price, we could write and execute the following query.
CREATE TABLE books (
isbn CHAR(13) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL,
description TEXT,
price DECIMAL(6,2)
);
2
3
4
5
6
Data manipulation
Data manipulation language (DML) statements are used for queries and data modification.
There are a lot of things that we could do with data. The actions that can be applied are sometimes abbreviated with CRUD. CRUD stands for Create, Read, Update and Delete.
Create
Creating data in SQL can be done with the INSERT INTO query. Next we add the columns that we want to add data to, and the values that should be stored in those columns.
INSERT INTO books (isbn, name, description, price) VALUES
("9781449303969", "Learning MySQL", "Good book", 33.50);
2
Read
Now that we have some data in the books table, lets read it back. This can be done using the SELECT query. The SELECT query is very powerful and deserves a chapter on its own. You can use it to filter, sort, group, join and many other operations. In this case we will just get the information from the columns named isbn, name, description and price.
SELECT isbn, name, description, price FROM books;
+---------------+----------------+-------------+-------+
| isbn | name | description | price |
+---------------+----------------+-------------+-------+
| 9781449303969 | Learning MySQL | Good book | 33.50 |
+---------------+----------------+-------------+-------+
2
3
4
5
Update
When we want to change existing data in a table, you can use the UPDATE query. The UPDATE query will provide the column name and value that you would like to change. In this case it is important to add a WHERE clause to the query to apply the change only to the book that has a specific isbn number. If you omit or forget the WHERE, all books will get the new price. This is mostly not what you would want.
UPDATE books SET price = 23.50 WHERE isbn = "9781449303969";
Delete
The last manipulation to data is the DELETE. With DELETE, we can remove data from the table. The DELETE will remove a full row in the table. Again it is important to use the WHERE clause to prevent deleting all rows, and thus all data in a table.
DELETE FROM books WHERE isbn = "9781449303969";